INTRODUCTION
} Disaster
management includes:
◦
Types of disasters
◦
How to prepare for
disasters?
◦
How to respond?
◦
If we are adequately
prepared it is possible to reduce an impact of a disaster.
} Impact
can be reduced by understanding of preventive actions, having knowledge of
certain lifesaving tools & techniques.
What is a disaster???
} “A
sudden accident or natural event that causes great damage or loss of life"
- Oxford Dictionary.
} A
serious disruption of the functioning of a society, causing widespread human,
material, or environmental losses which exceed the ability of the affected
society to cope using its own resources.”
HAZARD
} A
natural or human made event that threatens to adversely affect human life,
property or activity to the extent of causing a disaster.
} Disaster
Risk = Hazard +Vulnerability
RISK
} Risk
is a measure of the expected losses due to a hazardous event of a particular
magnitude occurring in a given area over a specific time period.
} Nature
of the Hazard
} Vulnerability
of the elements which are affected.
} Economic value of those elements.
VULNERABILITY
} It
is defined as “the extent to which a community, structure, service, and/or
geographic area is likely to be damaged or disrupted by the impact of
particular hazard, depending on their nature, construction and proximity to a
disaster prone area”
EFFECTS
} Physical:
Infrastructure damage
} Economic:
Power disruption, Water problems, Agricultural damage
} Social:
Telecommunication loss, poverty
} Emotional:
mortality
} Health: injuries, morbidity, epidemic
} Environmental:
Damage to inland and coastal environments, Flooding, Landslides
} Cultural:
Disruption of standard of living, lifestyle
} The
loss during the actual event is not necessarily be high, but, the losses become
very high due to inability to manage the situation in a timely manner and
inability to properly manage and secure the utilities, like: electricity, gas,
water etc.
WHY SHOULD WE STUDY??
} Asia-pacific
region: 60% of major natural disasters.
} India
manifests many natural disasters like floods, cyclones, landslides, earthquakes
etc. due to vast variation of geographical terrain and climatic conditions.
} INDIA:
2.4% of world’s land area. 7th largest country of the world with 15%
of the world’s population.
ARE WE PREPARED???
DISASTER MANAGEMENT
DEFINITION:
} Is
a systematic process that aims to reduce the negative impact or consequences of
adverse events.
DISASTER MANAGEMENT CYCLE
MITIGATION
} Mitigation
refers to all the actions taken before a disaster to reduce its impacts on
nation or community.
} mitigation=
prevention + preparedness
Four sets of tools that could be used to prevent or
mitigate disasters include:
a) Hazard
management and vulnerability reduction
b) Economic
diversification
c) Political
intervention and commitment
d) Public
awareness
PREPAREDNESS
} Measures
which enable government, organizations, communities and individuals to respond
rapidly and effectively to disaster situation.
Includes:
• Emergency
exercises/training
• Warning
systems
• Emergency
communications systems
• Evacuations
plans and training
• Emergency
personnel/contact lists
• Mutual
aid agreements
• Public
information/education
Disaster drills/ Mock tests
} Well
planned, organized and coordinated.
} Can
be scheduled periodic or unannounced.
RESPONSE
} Disaster
response is the sum total of actions taken by people and institutions in the
face of disaster.
} The
focus in the response phase is on meeting the basic needs of the people until
more permanent and sustainable solutions can be found.
} One
of the main goals of disaster management is the promotion of sustainable
livelihoods and their protection.
} Where
this goal is achieved, people have a greater capacity to deal with disasters
and their recovery is more rapid and long lasting.
Aims of disaster response
- To
ensure the survival of the maximum possible number of victims, keeping
them in the best possible health in the circumstances.
- To
re-establish self-sufficiency and essential services as quickly as
possible for all population groups.
- To
repair or replace damaged infrastructure and regenerate viable economic
activities.
- In
situations of civil or international conflict, the aim is to protect and assist
the civilian population, in close collaboration with the International
Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) and in compliance with international
conventions.
Disaster Response Activities
- Warning:
Evacuate or secure property
- Evacuation
and migration
- Search
and rescue
- Post-disaster
assessment: relief needs
- Relief:
material aid and emergency medical care
- Logistics
and supply
- Communication
and information management
- Survivor
response and coping: new and special needs
- Security:
rights and safety
- Emergency
operations management: Policies and procedures
- Rehabilitation:
resume functioning, assist victim’s self-help efforts.
- Reconstruction:
Permanent construction, services
- Revitalization
of the economy.
Recovery
} Returning
the community to normal.
} As
the emergency is brought under control growing number of activities aimed at restoring
their lives and the infrastructure that supports them.
Short-term recovery
} Restore
interrupted utility services, clear roads, temporary housing, public
information, health and safety education, provide food and shelter for those
displaced by the disaster. (few weeks)
Long-term recovery
} Complete
re-development of damaged areas for the community to return to a state that is equal
to or even better than it was before. (months- years)
Steps of recovery
- Gathering
basic information
- Organizing
recovery
- Mobilizing
resources for recovery
- Administering
recovery
- Regulating
recovery
- Coordinating
recovery activities
- Evaluating
recovery
Lifesaving tools AND techniques
VICTIM EVACUATION METHODS
} Required
to evacuate injured person from an emergency scene to a location of safety.
} Manual
carries are tiring for the rescuer and involve the risk of increasing the
severity of the casualty's injury.
} Choose
the evacuation techniques that will be least harmful, both to rescuer and the
victim.
Victim Drag and Carry Techniques
Tied-Hands Crawl
} Crawl
underneath a low structure.
} Victim
heavier than you, unconscious.
} Head
is not supported.
} Longer
distances to lift a victim safely.
One
Person Arm Carry
One
Person Pack-Strap Carry
Fire Man Carry
} Longer
distances.
Two
Person Carry (
by arms & legs)
Chair
Carry
} Carrying
victims up and down stairs or through narrow or uneven areas.
Ankle
Pull
} Fastest
method for moving a victim a short distance over a smooth surface.
Shoulder
Pull
} Preferred
over the ankle pull.
} Requires
the rescuer to bend over at the waist while pulling.
Blanket Drag
Preferred method for dragging a victim from confined
area.
Keep your back as straight as possible.
Use your legs, not your back.
Two Handed Seat
Four Handed Seat
Three Person Carry
} This
technique is for lifting a patient into a bed or stretcher, or for transporting
to short distances.
Improvised
Stretcher
Blanket
Stretcher
TRIAGE
} It
is the process of determining the priority of patient’s treatments based on the
severity of their condition.
} Useful
for rapid evaluation, allotment of priority for treatment and/or evacuation of
patients.
} Also
used in emergency departments.
Principles:
- Every
pt. should be received and triaged by appropriate, skilled health care
professionals.
- Triage
process shouldn’t cause a delay in the delivery of effective clinical care.
- Triage
is a clinical managerial decision and must involve collaborative planning.
Objectives
- Ensure
immediate medical intervention in life threatening situations.
- Expedite
the care of patients through a systemic initial assessment.
- Ensure
that patients are prioritized for treatment in accordance with the
severity of their condition.
- Decrease
the morbidity associated with medical conditions through early
intervention.
- Assist
pts. requiring treatment in another department and health care
institutions.
- Improve
public relations by communicating appropriate information to people
accompanying the pt.
- Improve
pt. flow
- Assist
in performance measurement.
COMPONENTS
Personnel
} Responsible,
knowledgeable, critical thinking, relevant history, phy. Assessment skills.
} Eg.
Drs., physio, nurses
Space requirement
} Large
enough to hold supplies, equipments and pts.
} Easily
accessible
Equipment and supplies
} Tailored
made for specific triage Rx. Protocols.
} Diagnostic
assessment tools
Communication and information
} Direct
link between incoming ambulances and other emergency vehicles.
} Closed
circuit TV monitoring.
} Computerized
information storage.
} Important
phone nos.
Documentation
} Pt’s
complaints, history, objective assessment, vital findings.
} Acuity
rating: life threatening, urgent, semi- urgent, referral
Triage scales
} Different
scales in peace and war situations
} Consider
factors such as extent of injury, time and distance to designated trauma
centers.
} Protocols
should be sensitive and specific.
} 1989
scale developed by Fitzgerald known as ‘Ipswich scale’
} Patient
should wait for medical care no longer than…..
|
TIME
|
COLOUR
|
|
Second
|
Red
|
|
Minute
|
yellow
|
|
An hour
|
green
|
|
Hours
|
blue
|
|
Day
|
white
|
|
CODE
|
Rx. REQUIRE
|
TRIAGE SCALE
|
SYMPTOMS
|
|
1
|
immediately
|
Resuscitation
(critically ill)
|
Unconscious, convulsing, extreme dyspnoea, CR
arrest/ shock
|
|
2
|
Within 10 min
|
Emergency
(at risk)
|
Severe pain due to any cause- MI, pul. embolism,
abdominal pain, dyspnoea, altered consciousness, trauma, sepsis
|
|
3
|
Within 30 min
|
Urgent
(significant illness/injury)
|
Moderate pain due to any cause-renal colic,
infection, head injury with transient loss of consciousness
|
|
4
|
Within 1hr.
|
Semi urgent
(sub-acute)
|
Mod./ chronic
symptoms- corneal foreign body, migraine headache
|
|
5
|
Within 2 hrs.
|
Non urgent
(chronic illness)
|
Symptoms of > 1wk. Duration
URTI, LBP
|
Special considerations
} Children
are up triaged routinely.
} In nuclear explosions:
} The
most seriously injured with multiple injuries and irradiation > 400 rads
should get last priority.
} 1st
priority is given to those who have a reasonable chance of survival.
CARDIO PULMONARY RESUSCITATION
(Basic life support)
(Basic life support)
} Aims
to restore airway, ventilation and circulation of the victims in cases of
airway obstruction, resp./ cardiac arrest,
with or without using equipments.
IMPORTANT STEPS IN BLS (2010)
} Initial
assessment to determine unresponsiveness
} Activation
of EMS
} C:
Circulation with ext. chest compression
} A:
Opening and maintaining an airway
} B:
providing ventilation through rescue breathing
} D:
Defibrillation with A.E.D
} Advance
care
STEPS IN C.P.R.
} Determine
unresponsiveness
} Call
for emergency dial
} Use
supine position/ log roll
C: Restoring Circulation
} Assess
pulselessness palpating major artery.
} PULSE
ABSENT- Ext. chest compression
Ext. chest compression
Serial, rhythmic pressure application over the lower
half of the sternum. (100bpm, 1.5 to2 inch)
A: Restore Airway
} Head
tilt chin lift technique
} Jaw
thrust manoeuvre
} Foreign
body removal
ABDOMINAL THRUSTS
(Heimlich manoeuvre)
(Heimlich manoeuvre)
} Forceful
thrust applied to an epigastrium to dislodge an obstruction.
} With
fist deliver quick upward and inward thrust.
B: Breathing
} Look
for chest movements.
} Listen
for air escaping during exhalation.
} Feel
for the flow.
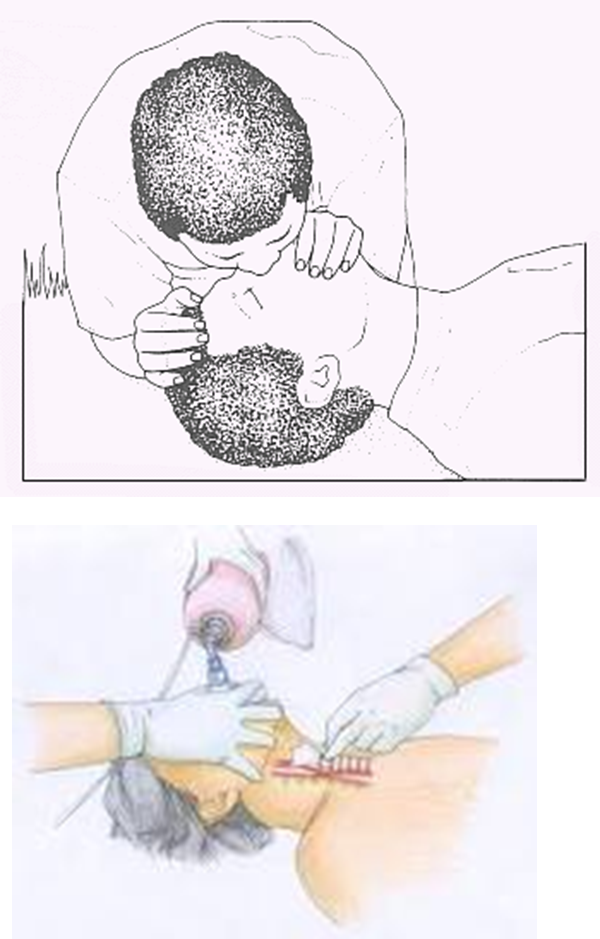
Restore ventilation
} Provide
artificial ventilation by
◦
Mouth to mouth
◦
Mouth to nose
◦
Mouth to mask
} Cricoid
pressure/ Sellick technique
D: Defibrillation (AED)
Universal steps of AED operation
} Step
1: power ON
} Step
2: attach electrode pads; one pad over upper Rt. sternal border and other lat.
to Lt. nipple.
} Step
3: clear the victim & press SHOCK button.
CPR Techniques:
Dr. Nishigandha Supekar (PT)
Dr. Komal Jakhotia (PT)
Dr. Apurv Shimpi (PT)





































Dear Apurva Shimpi, very good article actually presently i am doing research on Role of physiotherapy in disaster management. requesting for your mail to get your response on questionnaire.
ReplyDeletethank you
Very informative! 👍
ReplyDelete